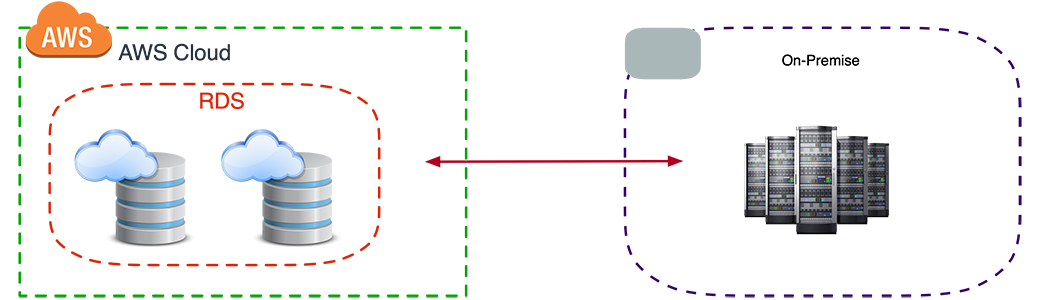
In a payment processor hybrid deployment with the database on the cloud and the transaction engine on-premises, businesses can leverage the advantages of both cloud services and on-premises infrastructure.
Storing the payment processor's database on the cloud allows for easy scalability and accessibility. Cloud databases can accommodate large volumes of transaction data, and their scalability features ensure that businesses can handle increased transaction loads without worrying about capacity limitations. Additionally, cloud databases can be accessed remotely, enabling authorized personnel to retrieve and analyze payment data from anywhere with an internet connection.
Storing the database on the cloud eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own on-premises database infrastructure. This can result in cost savings related to hardware procurement, maintenance, and software licensing. Cloud databases typically operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale their database usage and costs based on their actual needs.
Cloud databases often offer built-in redundancy and high availability features. They are designed to withstand failures and provide automated backups, data replication, and failover mechanisms. By utilizing a cloud database for payment data, businesses can ensure high availability and reliable disaster recovery capabilities, reducing the risk of downtime and data loss in case of unforeseen events.
In some cases, businesses may have specific data sovereignty or compliance requirements that mandate the storage and processing of payment data within a specific jurisdiction. By keeping the transaction engine on-premises, businesses can ensure that sensitive payment data remains within their controlled environment, adhering to local data privacy regulations and compliance frameworks.